🔋 Batteries on sale
What's behind the 2024 battery cost reductions and what impacts will it have?
Reports that CATL, the Chinese battery manufacturing giant, plans to slash its battery prices by 50% this year is sending shockwaves through the Electric Vehicle (EV) industry.
As batteries are essential not only for powering our vehicles but also for the broader energy transition, we will begin by exploring the various roles that batteries currently play. Following this, we will delve into battery pricing trends and discuss the implications of a potential 50% price cut.
Battery Applications
Most of us are familiar with AA batteries as they energize everyday devices like our TV remotes, toys and toothbrushes. But beyond these small-scale applications, batteries are also driving electric vehicles, powering homes (behind-the-meter), and serving critical functions on the electrical grid (utility scale).
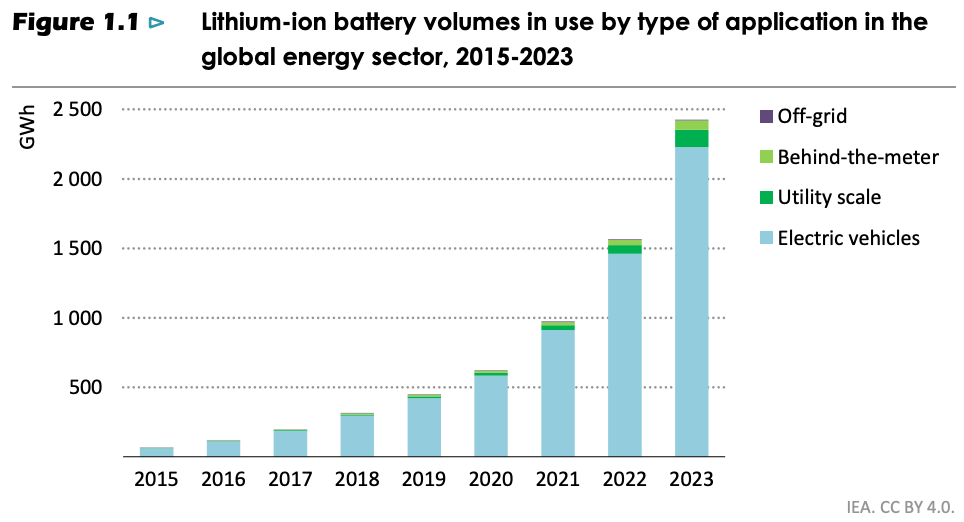
Batteries and Secure Energy Transitions, IEA April 2024 - Link. Lithium-ion batteries make up over 90% of the battery chemistry used in both EVs and grid storage systems.
Lithium-ion batteries are most used in electric vehicles, but their use in utility-scale and residential (behind-the-meter) applications is growing.
As solar and wind integration on the grid increases, batteries are proving increasingly valuable. By charging during periods of excess electricity production and discharging during peak demand, they offer significant financial gains through energy arbitrage—buying low and selling high.
Flash sale or long-term trend?
Having explored the primary applications of batteries in electric vehicles (EVs) and stationary storage, let’s turn our attention to prices. Since 2010, lithium-ion battery pack and cell prices have been consistently decreasing by about 13% each year.
Batteries and Secure Energy Transitions, IEA April 2024 - Link.
The news of the potential 50% battery price drop is probably due to a mix of supply chain savings (the 6x lithium price jump of 2022 did not help), and manufacturing cost reductions, but how come it is much higher than the average 13% yearly price decrease?
CATL might be using a pricing strategy to undercut the competition and expand its market share, even if it means selling at a loss. By lowering their prices, other manufacturers are pressured to follow suit, and those unable to innovate and reduce costs may find themselves struggling to survive.
And what about demand?
A low pricing strategy can be used to expand the market share, but it can also boost demand. The idea is that even if the profit margins decline, profits can be recouped by increasing sales of a cheaper product.
In the EV space, costs will probably come down, as batteries represent a significant portion of the car production costs. However, because some countries (EU and USA) are at cutthroat trade wars with China, the price drop might not be reflected worldwide. Furthermore, demand growth expectations also have to be counterbalanced by the fact that high interest rates are hurting the consumer’s ability to spend. (Tesla reported a 9% drop in car deliveries in Q1 2024).
While there are some uncertainties about demand growth on the consumer EV side, it’s important to note that CATL isn't solely an electric vehicle battery producer; they also manufacture batteries for stationary storage. In this sector, I believe that as battery prices decrease, the likelihood of demand growth increases.
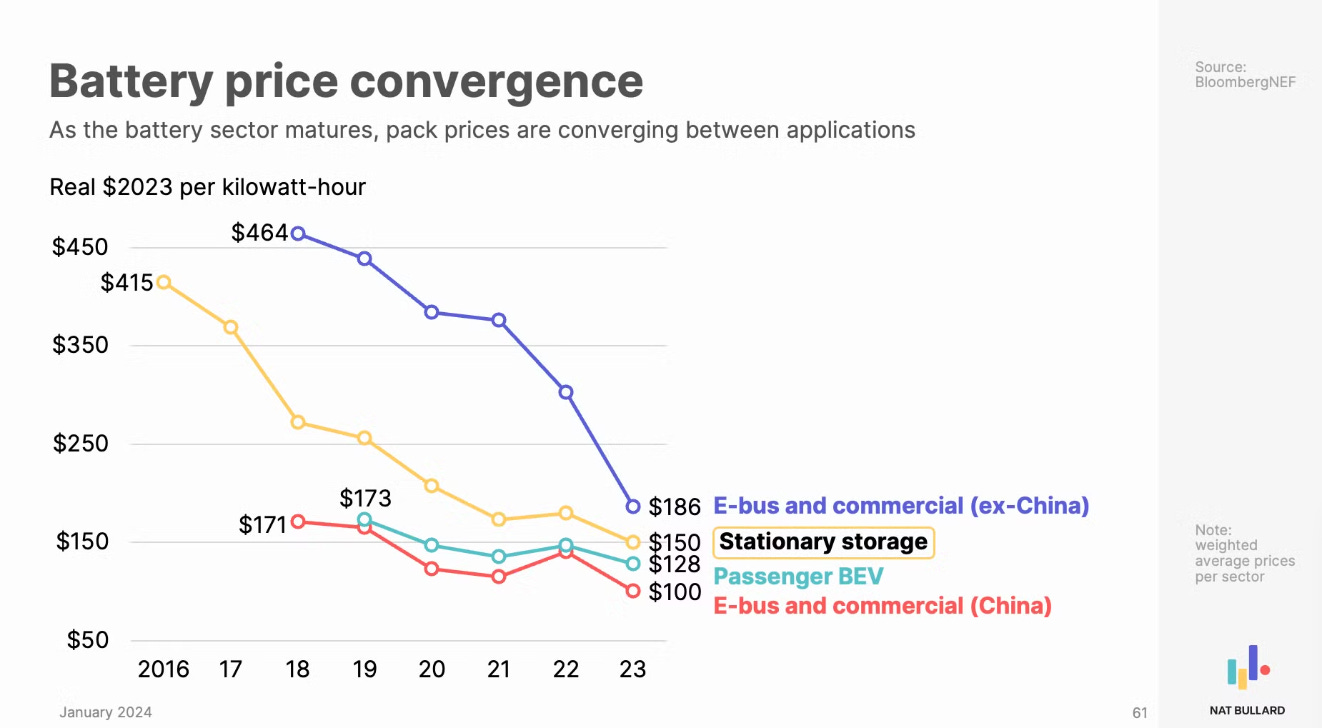
Nat Bullard Annual presentation slide 6, highlighting the link between battery prices accross sectors.
In stationary storage, the battery itself constitutes the entire end product, unlike in EVs. This means that any reduction in battery pack costs has a more direct and substantial impact on the final product prices. Additionally, as previously discussed, the increasing integration of Variable Renewable Energy (VRE) sources in the grid, such as wind and solar, enhances the overall value of batteries.
With the value of batteries rising and their costs decreasing, it's no coincidence that most new renewable energy projects now include battery storage systems.
Conclusion
Our discussion began with the news of CATL's significant price reduction, which appeared to stem from improvements in the supply chain and advancements in manufacturing. However, when viewed against the backdrop of historical price trends, this 50% price drop stands out, prompting us to explore other potential drivers and consequences of such a dramatic reduction.
We identified that this price reduction could also be a strategic move to capture more market share and stimulate demand. On the demand side, we observed that due to technical advancements and macroeconomic trends, the effects of battery price reductions are likely to be more pronounced in the residential and utility storage sectors.
This opens up the question, in the face of the urgency of the energy transition, should we fear or embrace China’s price cuts?
🔗 - Check these out
To help you answer the opening question, I invite you to listen to some great insights in this short 10 minutes podcast from Redefining Energy.
Learn all about batteries on this great educational website: Battery University.